Skills & Competencies
This page presents the engineering competencies developed during my first year of the BUT GEII program, mainly through project-based learning (SAÉ), laboratory work and supervised practical sessions.
In the first year, the training focuses primarily on two core competencies: Conceiving and Verifying technical systems.
Competency-based learning in BUT GEII
In the BUT GEII program, learning is structured around competencies rather than isolated subjects. These competencies are developed and assessed through SAÉ (Situations d’Apprentissage et d’Évaluation), where students work autonomously on technical projects close to real engineering situations.
Each project requires understanding a technical objective, proposing solutions, implementing them, and validating their correct operation. This portfolio is therefore an integral part of the learning and evaluation process.
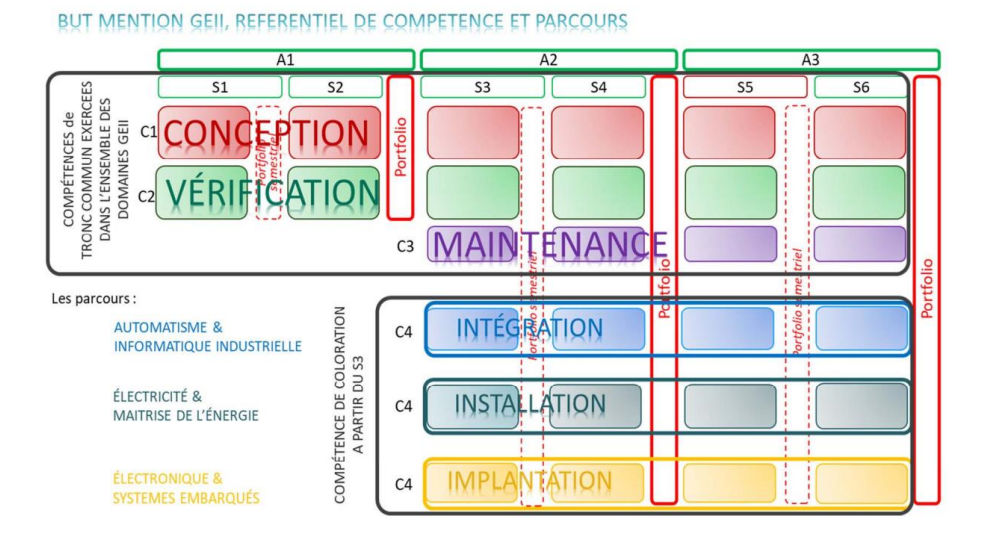
Competency-based approach used in the BUT GEII program
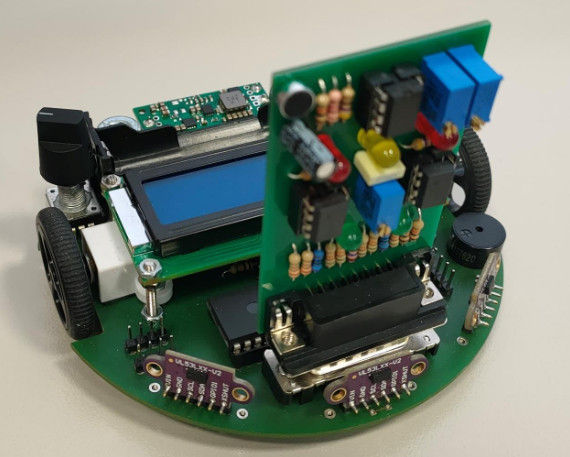
Design phase — electronic schematics and functional analysis (SAE 1.01)
C1 — Conceive
During the first year, the competency Conceive focuses on understanding a technical problem and proposing a coherent solution. This includes analyzing requirements, structuring ideas, and formalizing solutions.
In the SAE 1.01 (Line-following robot), this competency was strongly mobilized. Starting from a technical contract, we designed our own electronic board, performed a functional analysis, created electrical schematics, and prepared the PCB layout.
Compared to other projects, this SAE required conceiving a system almost from scratch, which made the design phase particularly important.
C2 — Verify
The competency Verify consists in checking that a designed system behaves as expected and complies with the given requirements. Verification involves testing, debugging, and correcting errors.
In SAE 1.02 (Automation), verification played a central role. We tested logic diagrams created in TIA Portal directly on a real Siemens S7-1200 PLC, using indicator lights, push buttons, emergency stops and actuators such as a fan.
Errors in logic equations, wiring or safety conditions had to be identified and corrected through supervised testing sessions.
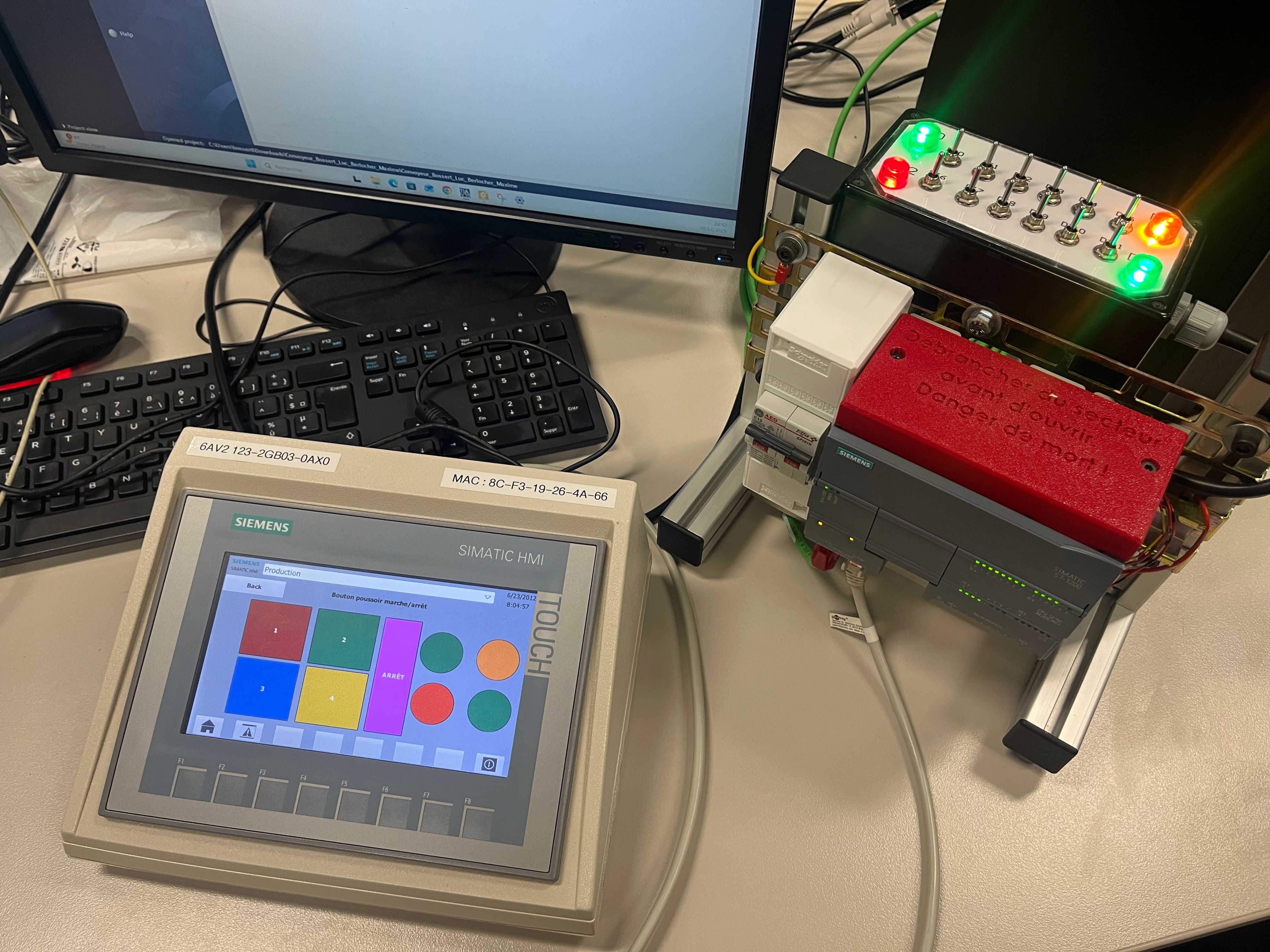

Verification phase — testing PLC programs on real hardware (SAE 1.02)
Current level and perspective
As a first-year BUT GEII student, my current focus is on learning rigorous engineering methods, understanding how to structure a technical solution, and validating basic systems through testing.
These competencies in Conceiving and Verifying are still in development and will be progressively deepened during the next semesters through more complex projects and systems.